Introduction: What is Agentic AI?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, Agentic AI has emerged as a game changer, especially for industries that thrive on dynamic decision-making, personalization, and process automation. Unlike traditional AI models that follow pre-defined rules or respond reactively to user prompts, Agentic AI represents systems that act autonomously, proactively identifying tasks, setting goals, and pursuing them independently. These AI agents don’t just process information—they take action.
For ecommerce businesses, Agentic AI offers a massive leap in operational efficiency and customer experience. From autonomously launching marketing campaigns to optimizing inventory or personalizing customer journeys, Agentic AI transforms digital storefronts into self-learning, self-optimizing ecosystems.
Components of Agentic AI
“Agentic AI is the first technology that can think and act on its own, combining creativity, action, learning, and autonomy—something no single tool like chatbots, automation, or even generative AI can fully achieve“
To truly understand what makes Agentic AI unique, it’s important to break it down into its key components and compare them with other common technologies like chatbots, automation, and generative AI. The table below serves as a beginner-friendly guide:
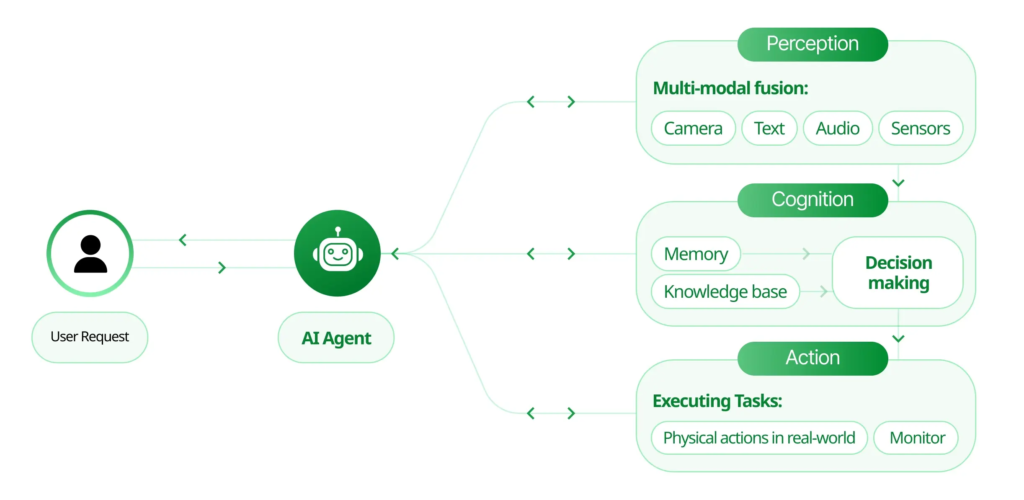
| Component | What It Means | Example in Ecommerce | How It’s Different from Chatbots, Automation & Generative AI |
| Perception | Ability to sense and understand what’s happening around it using data from multiple sources (e.g., web, sales, inventory, social media). | The AI agent monitors competitors’ prices, customer reviews, weather, and social media to spot trends. | Chatbots only respond to direct customer queries. Automation only works when triggered. |
| Goal-setting | Defining its own objectives based on what it perceives. | If the agent notices a sudden interest in eco-friendly products, it sets a goal to promote green products across channels. | Automation doesn’t set its own goals—it follows rules pre-set by humans. |
| Planning | Designing a step-by-step approach to achieve a goal. | The agent plans a campaign: identifying which eco-products to promote, creating discount offers, and selecting channels (email, website banners, social ads). | Chatbots don’t plan—they only reply. Generative AI can create content but needs humans to direct it. |
| Action-taking | Executing the plan autonomously across systems. | The AI launches the campaign automatically and adjusts pricing in real-time based on performance. | Automation can act, but only if it’s told exactly what to do upfront. Agentic AI acts based on its own plans. |
| Learning & Feedback | Evaluating outcomes, learning from success or failure, and refining future plans. | The agent sees that eco-friendly products sell well when bundled with free shipping, so it adopts this as a future tactic. | Automation doesn’t learn—it repeats the same task. Generative AI doesn’t self-evaluate outcomes. |
| Decision-making Autonomy | Ability to decide what to do next without human intervention. | The agent decides to run a survey to understand what other green products customers want, without anyone telling it to do so. | Chatbots can’t make independent decisions. Generative AI only responds to requests. |
Think of Agentic AI as a highly capable digital manager that can:
- Observe your business environment
- Set its own tasks (like planning sales campaigns)
- Act across platforms (launch promotions, adjust prices, update inventory)
- Learn from results (what worked, what didn’t)
- Continuously improve its approach
In contrast:
| Technology | What It Does |
| Chatbot | A digital receptionist that waits for customers to ask something, then responds based on scripts. |
| Automation | A digital worker that follows step-by-step rules you define (e.g., send a thank-you email after purchase). |
| Generative AI | A creative assistant that generates text, images, or videos when asked, but doesn’t know when or why to create them unless directed. |
Defining Agentic AI: The Basics
At its core, Agentic AI refers to AI models endowed with agency, the ability to:
- Observe their environment
- Plan actions towards a goal
- Act independently
- Learn from outcomes
- Iterate for improved results
Traditional AI relies on inputs from humans to trigger responses. For example, a chatbot only replies when a customer sends a message. Agentic AI, on the other hand, can proactively detect emerging trends, suggest new actions, and even trigger workflows without direct human involvement.
Let’s look at Agentic AI in Ecommerce Vertical
Ecommerce is a fast-paced industry driven by:
- Constantly shifting consumer preferences
- Highly competitive pricing
- Personalized experiences
- Complex supply chains
- Multichannel interactions
Traditional AI, while useful, has always been reactive—responding to customer queries, providing recommendations when prompted, or forecasting sales based on historical data. However, Agentic AI takes this further, transforming ecommerce from reactive to proactive and predictive.
Agentic AI in Action: Ecommerce Examples
1. Autonomous Product Recommendations
Traditional recommendation engines suggest products based on customer history and browsing data. Agentic AI goes further—it monitors broader market trends, inventory levels, weather, social sentiment, and more to anticipate customer needs before they even visit your site.
For example, if a fashion ecommerce platform’s agent detects rising social media buzz around pastel summer dresses, it can:
- Automatically promote relevant inventory on the homepage.
- Suggest complementary items like sandals or hats.
- Notify the procurement team to stock up.
This continuous sensing-action loop boosts relevance and revenue.
2. Dynamic Pricing & Competitive Intelligence
Pricing in ecommerce is a constant tug-of-war between profitability and competitiveness. Traditional AI models optimize prices based on sales trends or seasonal data. Agentic AI takes this further by:
- Monitoring competitor pricing in real-time.
- Tracking global commodity costs for raw materials.
- Detecting shifts in customer sentiment (e.g., price sensitivity in a downturn).
- Automatically adjusting prices to maximize margins while staying competitive.
The AI agent doesn’t wait for a human to analyze a pricing dashboard—it continuously acts and refines its strategy.
3. Proactive Customer Service & Retention
In traditional ecommerce, customer service is largely reactive—responding to complaints, tracking orders when customers inquire, or offering discounts when churn seems imminent. Agentic AI can predict and act before issues escalate. Examples include:
- Identifying at-risk customers based on behavioral signals (frequent cart abandonment, slow browsing, customer service interactions).
- Triggering personalized offers or proactively dispatching order updates before customers ask.
- Detecting potential delivery delays and suggesting alternatives (such as pickup at a nearby store or faster shipping options).
This makes customer service a proactive revenue protector, rather than a cost center.
4. Autonomous Marketing Campaigns
Marketing teams today are heavily reliant on data analytics, but launching campaigns still involves manual work—segmentation, asset creation, channel selection, and performance tracking. Agentic AI can take over much of this workload by:
- Detecting emerging trends.
- Automatically generating creatives using Generative AI.
- Selecting optimal audience segments.
- Launching and continuously optimizing campaigns across channels—without human intervention.
For example, if an AI agent notices a sudden spike in organic traffic for hiking gear, it can instantly:
- Create ad copies targeting outdoor enthusiasts.
- Launch campaigns on social, search, and email.
- Monitor performance and dynamically adjust creatives and bidding strategies.
5. Smart Inventory & Supply Chain Automation
Inventory management is a critical pain point in ecommerce. Overstock ties up capital; understock frustrates customers. Agentic AI brings real-time intelligence to this process:
- Predicting demand based on external signals (weather, global events, emerging trends).
- Suggesting or autonomously placing purchase orders.
- Recommending pricing changes to move slow-moving stock.
- Triggering marketing campaigns to clear inventory.
This self-regulating supply chain reduces waste and boosts profitability.
Key Technologies Enabling Agentic AI in Ecommerce
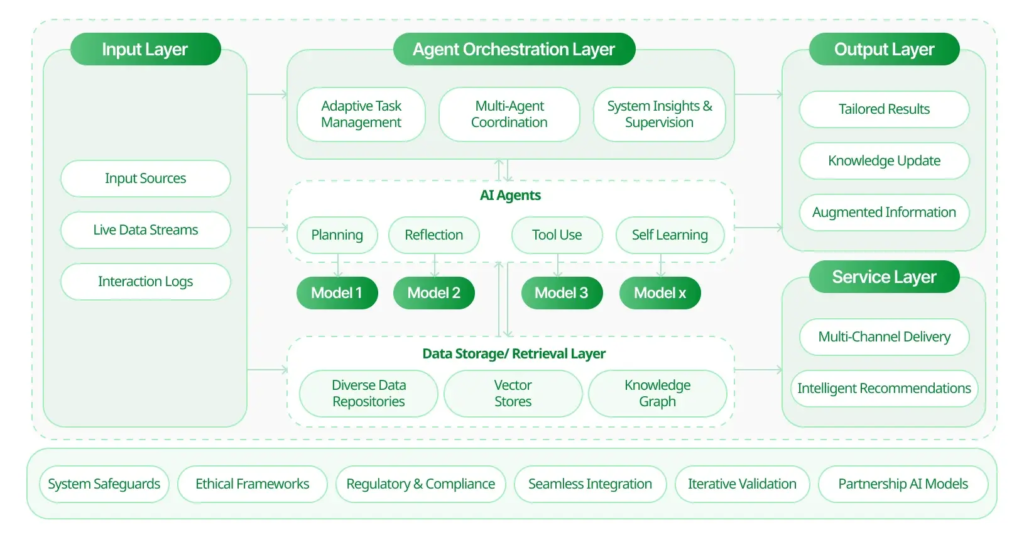
To make this possible, Agentic AI leverages a fusion of technologies:
| Technology | Role in Agentic AI for Ecommerce |
| Large Language Models (LLMs) | Understanding customer language and context across reviews, queries, and social chatter. |
| Generative AI | Creating marketing copy, product descriptions, and creative assets dynamically. |
| Reinforcement Learning | Learning optimal pricing, campaign strategies, and product placements through trial and error. |
| Multimodal AI | Processing diverse inputs (images, text, video, voice) to understand customer intent. |
| Real-time Data Streams | Continuously monitoring competitor prices, social sentiment, and global events. |
| Automation Platforms | Directly triggering backend actions like inventory reorders or campaign launches. |
Challenges in Deploying Agentic AI for Ecommerce
Despite its promise, deploying Agentic AI comes with hurdles:
- Data Fragmentation: Ecommerce data lives across multiple silos—CRM, ERP, PIM, analytics tools. Agents need unified access to all this data.
- Trust & Explainability: Autonomous decisions need clear audit trails. Retailers want to know why the AI acted in a particular way.
- Ethics & Bias: Agents could unintentionally reinforce biases (e.g., promoting only popular brands or neglecting smaller sellers).
- Over-automation Risks: Customers might resist if interactions feel overly robotic. Maintaining a human touch is critical.
Preparing for the Agentic AI Future in Ecommerce
For ecommerce leaders looking to embrace Agentic AI, here’s a roadmap:
1. Consolidate Data into a Unified Layer
Ensure product, customer, marketing, and operational data is accessible to your AI agents.
2. Start with Low-risk Automation
Begin with back-office processes like inventory management or pricing. Gradually move to customer-facing areas.
3. Build a “Human-in-the-loop” Framework
Ensure critical decisions (e.g., deep discounts, VIP offers) still involve human oversight until confidence grows.
4. Experiment & Iterate
Run pilot projects in specific categories, such as fashion or electronics, where trends shift quickly and Agentic AI can demonstrate quick wins.
5. Establish Governance
Define clear guidelines around bias mitigation, transparency, and ethical boundaries for autonomous decision-making.
Agentic AI is the Future of Smart Ecommerce
Agentic AI marks the evolution from predictive analytics to autonomous action. It allows ecommerce players to stay ahead of trends, anticipate customer needs, and act at machine speed—without constant human input.
For ecommerce players facing thin margins and relentless competition, Agentic AI isn’t just a tool—it’s a survival strategy. As technology evolves, agentic storefronts could become the new standard, with digital stores running themselves, optimizing every touchpoint, and evolving based on continuous learning.
Whether you’re a global marketplace or a niche D2C brand, understanding and embracing Agentic AI today will determine your competitive edge tomorrow.

Leave a Reply